What is the Antiderivative of Tan 2x?Integral of tan^2 (x) \square! For a function f and an antiderivative F, the functions F(x) C, where C is any real number, is often referred to as the family of antiderivatives of f For example, since x2 is an antiderivative of 2x and any antiderivative of 2x is of the form x2 C, we write ∫2xdx = x2 C

Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像
Tan^2x antiderivative
Tan^2x antiderivative- The cos2(2x) term is another trigonometric integral with an even power, requiring the powerreducing formula again The cos3(2x) term is a cosine function with an odd power, requiring a substitution as done before We integrate each in turn below cos3(2x) = cos2(2x)cos(2x) = (1 − sin2(2x))cos(2x)Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functions For more about how to use the Integral Calculator, go to "Help" or take a look at the examples




Find The Antiderivatives Of The Following 1 Gauthmath
The secant of x is 1 divided by the cosine of x sec x = 1 cos x , and the cosecant of x is defined to be 1 divided by the sine of x csc x = 1 sin xEvaluate {eq}\displaystyle \int (2 x 4x^3 \tan^2 x 1)\ dx {/eq} Indefinite integral An indefinite integral is also referred to as the primitive integral, inverse derivative, antiderivativeFind the AntiDerivative 2x Write as a function The function can be found by finding the indefinite integral of the derivative Set up the integral to solve Since is constant with respect to , move out of the integral By the Power Rule, the integral of with respect to is
Integral of tan^2 (x) \square!Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integral of sin(x), integ
This is very easy, and this involves the use of trig identities math\displaystyle \int \tan ^2\left(x\right)\,dx/math Since math\tan ^2\left(x\right)=1\sec ^2\left(x\right)/math, so we rewrite the equation as mathPeople Also Asked, what is the integral of tan 2 x? Get an answer for 'Prove the following reduction formula integrate of (tan^(n)x) dx= (tan^(n1)x)/(n1) integrate of (tan^(n2))dx' and find homework help for other Math questions at



How To Integrate X Tan 2 X Dx Quora
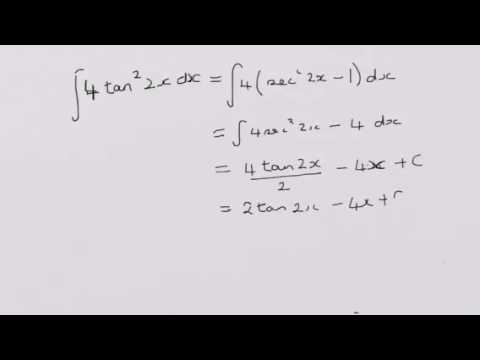



Integrating Tan 2 2x Youtube
tanxand the general antiderivative of sec2x is tanxC What is integration of SEC 2x?, Answer (1/2) log sec 2x tan 2x C, where C is the constant of integration Furthermore, What's the integral of secant squared?, The integration of secant squared of angle function with respect to is equal to sum of the tan of angle and the constant of integration$$\int sec^2x \tan^2x dx = tan^2x 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx$$ You can move the $ 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx$ to the left hand side of the equation by addition $$\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx= tan^2x c, c\in\mathbb{R}$$ Note that once we have a side without an integral on it you need to include a constant of integration By Staff Writer Last Updated Follow Us The antiderivative of tan (x) can be expressed as either ln cos (x) C or as ln sec (x) C In these equations, C indicates a constant, ln is the natural logarithm function, cos indicates the function cosine and sec denotes the function secant Both solutions for the antiderivative of tan (x) can be found by using an



1



Integrate Tanx Dx Studyrankersonline
©05 BE Shapiro Page 3 This document may not be reproduced, posted or published without permission The copyright holder makes no representation about the accuracy, correctness, orAntiderivative of 2tan x sec x Compute tan x sec 2 x dx in two different ways a) By substituting u = tan x b) By substituting v = sec x c) Compare the two results Solution a) Compute tan x sec 2 x dx by substituting u = tan x If u = tan x 2then du = sec x dx and tan x sec 2 x dx = u du = 1 u2 c 2 = 1 tan2 x c 2The Integral Calculator supports definite and indefinite integrals (antiderivatives) as well as integrating functions with many variables You can also check your answers!



10 4 Integration Of Powers Of Trigonometric Functions




Trigonometric Integrals
The given integral I = ∫ tan 3 2x sec 2x dx = ∫ tan 2 2x sec 2x tan 2xdx = ∫ (sec 2 2x 1)sec2x tan 2xdx Let sec 2x = u 2sec2x tan2xdx = du ← Prev Question Next Question → Related questions 0 votes 1PDF 檔案1− x2 Then the full antiderivative is arcsinx 2 2x √ 1− x2 4 = arcsinx 2 x √ 1−x2 2 C 6 Chapter 10 Techniques of Integration This type of substitution is usually indicated when Prove that the derivative of tan(x) is sec^2(x) y=xx^22x^3 Curve has a stationary point at the point M where x=2Hey again Question Use the identity sec^2 x=tan^2 x 1 and the substitution tanx=u to find INT tan^4 x dx please help me step by step t




Integration Calculus 2
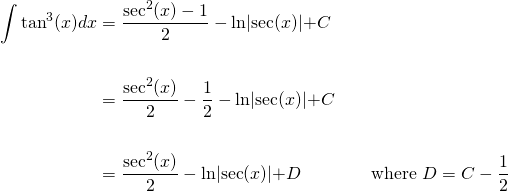



Integral Of Tan 3 X Steemit
This integral is discussed in most calculus books I will write a detailed solution, because thinking about this integral gives a good workout in techniques of integration You have already been told about the useful identity $$1\tan^2 x=\frac{1}{\cos^2 x}$$ You may have seen this identity as $$1\tan^2x =\sec^2 x$$Free antiderivative calculator solve integrals with all the steps Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experienceIntegration is an important tool in calculus that can give an antiderivative or represent area under a curve The indefinite integral of , denoted , is defined to be the antiderivative of In other words, the derivative of is Since the derivative of a constant is 0, indefinite integrals are defined only up to an arbitrary



9htgln45fv Ehm




How Do You Integrate Int Sec 1 X Tan 1 X Dx Socratic
Proof of Integral of sec²x formula Take x as a variable, and it also represents angle of a right triangle According to trigonometry, the secant squared of angle x is written as sec 2 x in mathematical form The indefinite integration of secant squared function with respect to x is written mathematically as followsGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Since the derivative of sec(x) sec ( x) is sec(x)⋅tan(x) sec ( x) ⋅ tan ( x), the integral of sec(x)⋅tan(x) sec ( x) ⋅ tan ( x) is sec(x) sec ( x) sec(x)C sec ( x) C The answer is the antiderivative of the function f (x) = sec(x)⋅tan(x) f ( x) = sec ( x) ⋅ tan ( x) F (x) = F ( x) = sec(x)C sec ( x) C




Find The Indefinite Integral Integral Sec 5 2x Tan Chegg Com



Math Problems Simplifying With Trigonometry Identities And Then Integration
Answer to Determine the integral int_{0}^{pi/4} tan^2x dx By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework 2 The attempt at a solution ∫tan x ∫tan 2 x HallsofIvy said I presume it was a typo, but of course, " " is NOT " " Just to set the record straight, ∫tan 3 x dx ≠ ∫tan x dx ∫tan 2 x dx I think that's what HallsOfIvy was attempting to say, but omitted the exponent on the second integralHow to integrate tan^2 x



Integral 2
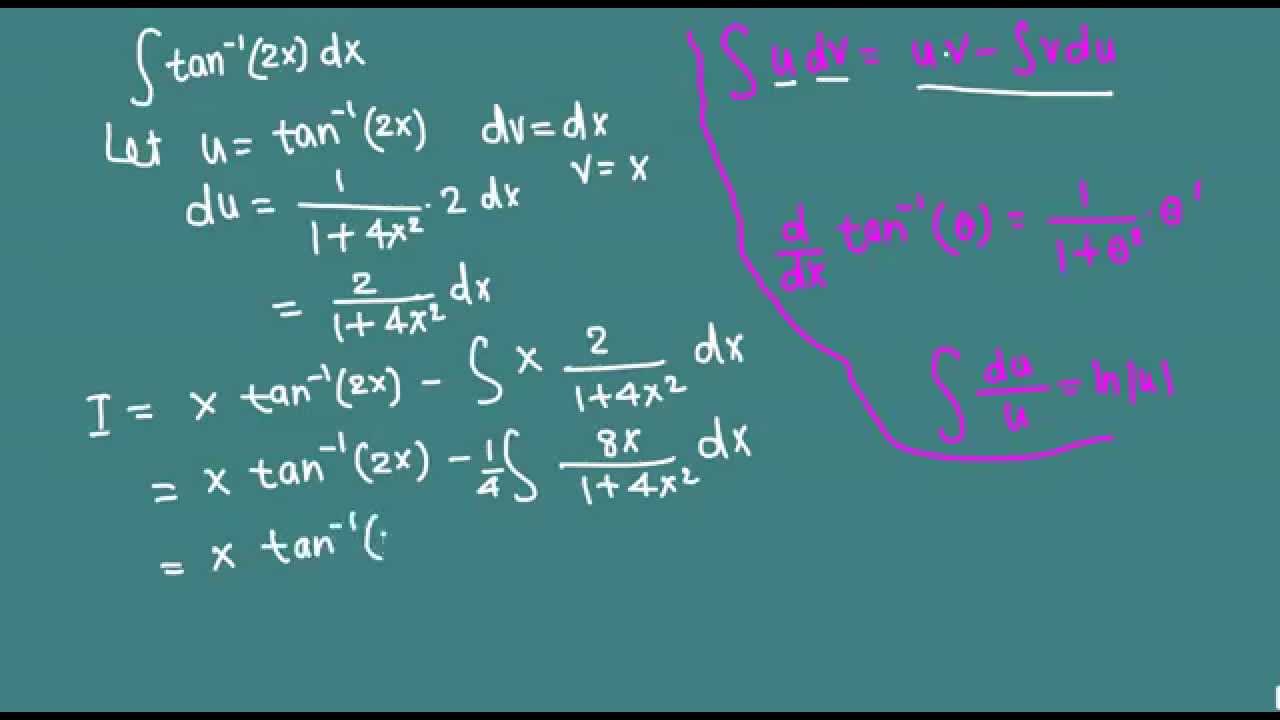



Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube
The second derivative of tan^2x is 4sec 2 (x)tan 2 (x) 2sec 4 (x) Interesting property of the derivative of tan^2x It is interesting to note that the derivative of tan 2 x is equal to the derivative of sec 2 x The derivative of > tan 2 xThis video goes through the integral of tan^2(2x) This type of integral would typically be found in a Calculus 1 class PLEASE NOTE Formula written in thFind the antiderivative of tan^2 (x) dx Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students




Integrate Tan 2x By Parts




Sorry For This Question But Is Tan 2x 3 The Same With Tan 2x 3 Or No Because My Classmates Differentiated This By Changing Tan 2x 3 To Tan 2x 3 Because I Don T Know Any
Tan^2x antiderivativeCalculate the indefinite integral of the function y = tan^4x tan^2x 2 Educator answers Math Latest answer posted November 23, 10 at AMSee the answer How do you solve this integral of 3 sec(2x1)tan(2x1)?Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreI tried it first using u = tan^2x like steve05 said which worked I also tried it using u = tanx which worked out to be tan^3x/3 really easily too Much simpler than I thought



What Is The Integral Of Tan X 2 Quora




Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia
Integral of tan^2 x sec^6 x dx Question Evaluate the following $$\int \tan^2x\sec^6x\text{ d}x $$ Evaluating Indefinite Integral The antiderivative of a function is the result of evaluating anAs there is no way to immediately integrate tan^2 (x) using well known trigonometric integrals and derivatives, it seems like a good idea would be writing tan^2 (x) as sec^2 (x) 1 Now, we can recognise sec^2 (x) as the derivative of tan (x) (you can prove this using the quotient rule and the identity sin^2 (x) cos^2 (x) = 1), while we get x when we integrate 1, so our final answer is tan In this video, I demonstrate how to find the antiderivative or the integral of tan^2(x) This would normally be quite a difficult integral to solveHowever,




How Do You Integrate 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Socratic




What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora
Explanation Perform a substitution u = 2x, ⇒, du = 2dx The integral is I = ∫arctan(2x)dx = 1 2 ∫arctanudu Perform an integration by parts ∫f g'dx = f g − ∫f 'gdx Here,Clearing cache Cache cleared1 2x x2 12 Which of the following is an antiderivative of the function f(x) A tan1(x – 1) C B – tan'(x – 1) C C – tan1x C D tanlx² C
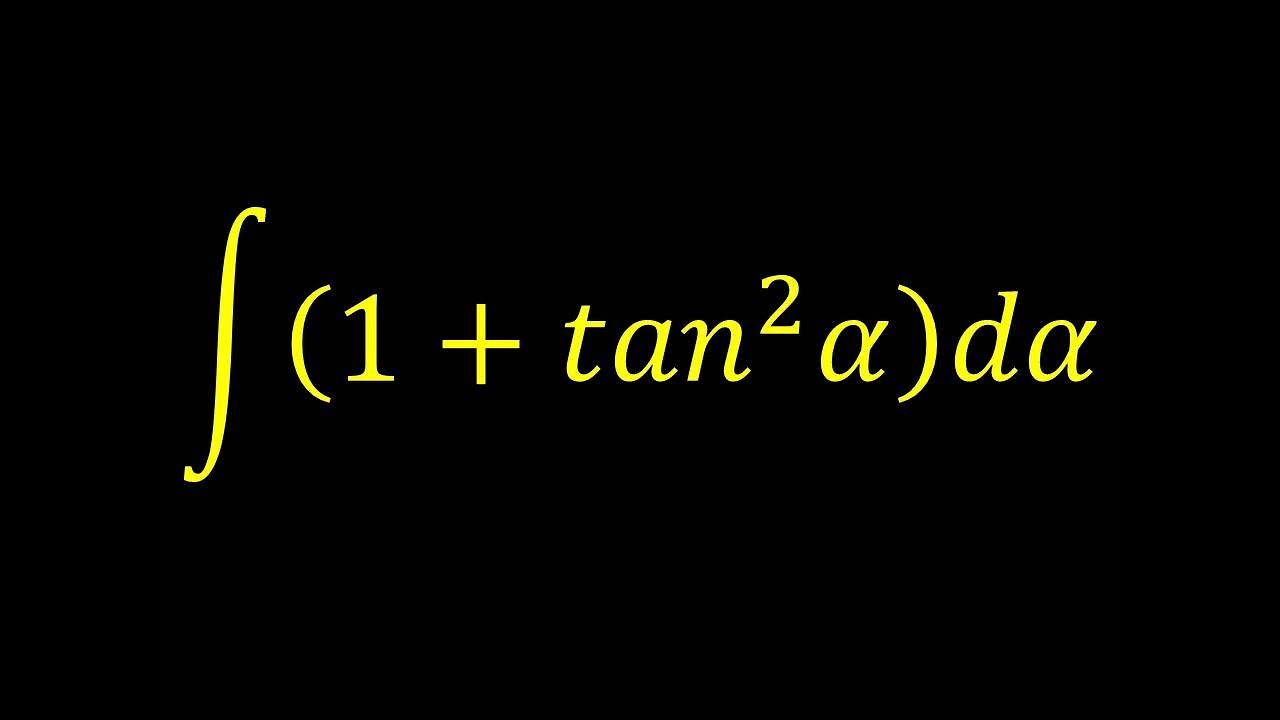



Integral Of 1 Tan 2 X Integral Example Youtube
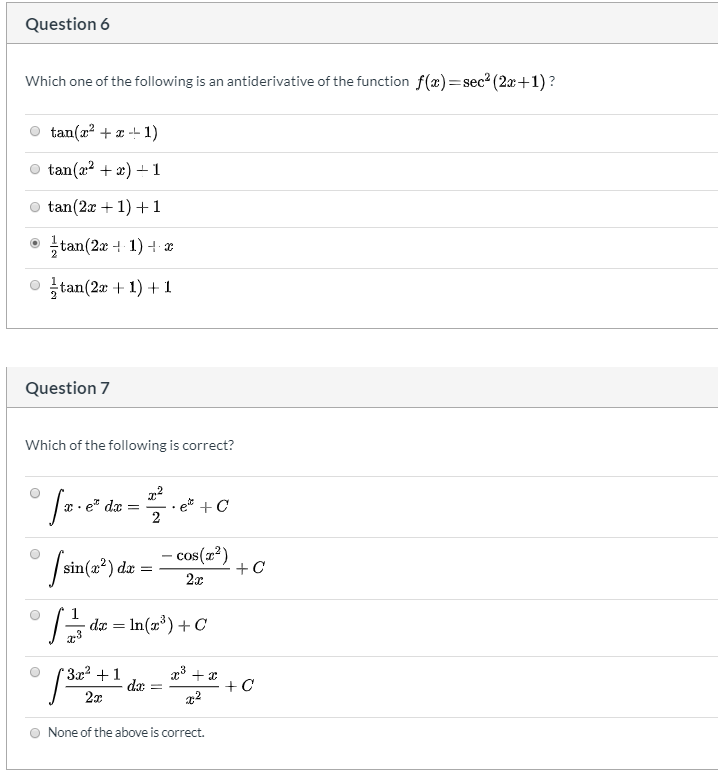



Question 6 Which One Of The Following Is An Chegg Com
2 Answers The answer is tanx−xc What is SEC equal to?\\int \tan^{2}x\sec{x} \, dx\ > < Antiderivative of tan^2xDerivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp Conic Sections TransformationIf it's not what You are looking for type in the derivative calculator your




Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube
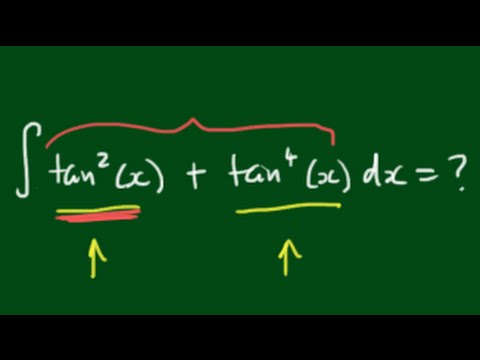



Evaluating The Integral Tan 2 X Tan 4 X Dx Youtube
To calculate online an antiderivative of composition of functions of the form u(axb), where u is a usual function, simply type mathematical expression that contains the function, specify variable and apply function antiderivative_calculator For example, to calculate online an antiderivative of the following function `exp(2x1)` you must enter antiderivative_calculator(`exp(2x1);x`), after calculating the result `exp(2xThanks for the A! Use the half angle formula, sin^2(x) = 1/2*(1 cos(2x)) and substitute into the integral so it becomes 1/2 times the integral of (1 cos(2x)) dx Set u = 2x and du = 2dx to perform u substitution on the integral Since dx = du/2, the result is 1/4 times the integral of (1




Find The Antiderivatives Of The Following 1 Gauthmath
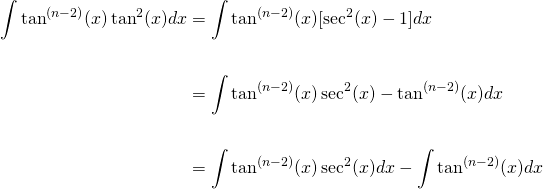



Reduction Formula For The Integral Of Tan N X Dx Steemit
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!This would normally be quite a difficult integral to solve However, the ever powerful trigonometric identities make this an easy problem By realising that tan^2(x)=sec^2(x) – 1, the integration of these two terms evaluates to tan(x) – x Thanks for watching Braking it into two integrals ∫ t a n 3 ( x) s e c 2 ( x) d x − ∫ t a n 3 ( x) d x For the first integral, substituting u = tanx, du = sec^2 (x) dx which takes care of the right half of it ∫ u 3 d u = u 4 4 = t a n 4 ( x) 4 Now for the second integral from several steps above Breaking it down to take out a tangent to get a tan




Download Antiderivative Of Tan 2x Mp3 Mp4 Free All Ques Mp3



1




What Is The Integral Of 1 Tan2x Quora
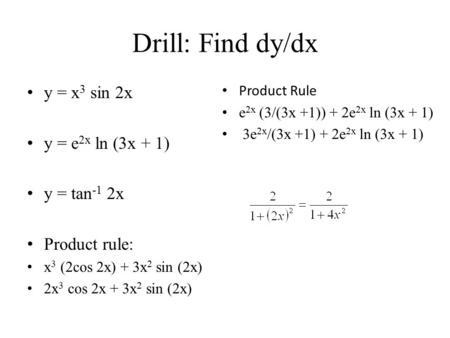



6 2 Antidifferentiation By Substitution Ppt Download




Finding The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Powers Of Trigonometric Functions




What Is The Integral Of Cos 2x Cos Square X




Please Integrate This And Send Me The Solution Maths Doubts Goiit Com
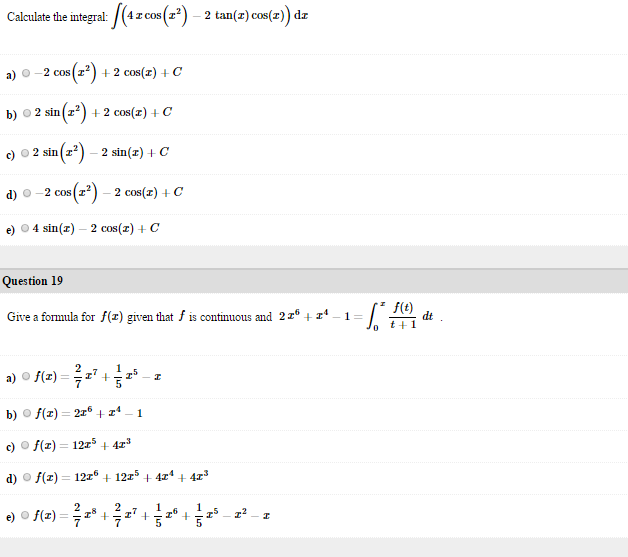



Calculate The Integral Integrate 4x Cos X 2 2 Chegg Com




Mathwords Integration By Parts




Calculate The Given Indefinite Integral Integrate Chegg Com



Http Professormike Pbworks Com W File Fetch 7 2 Pdf



2
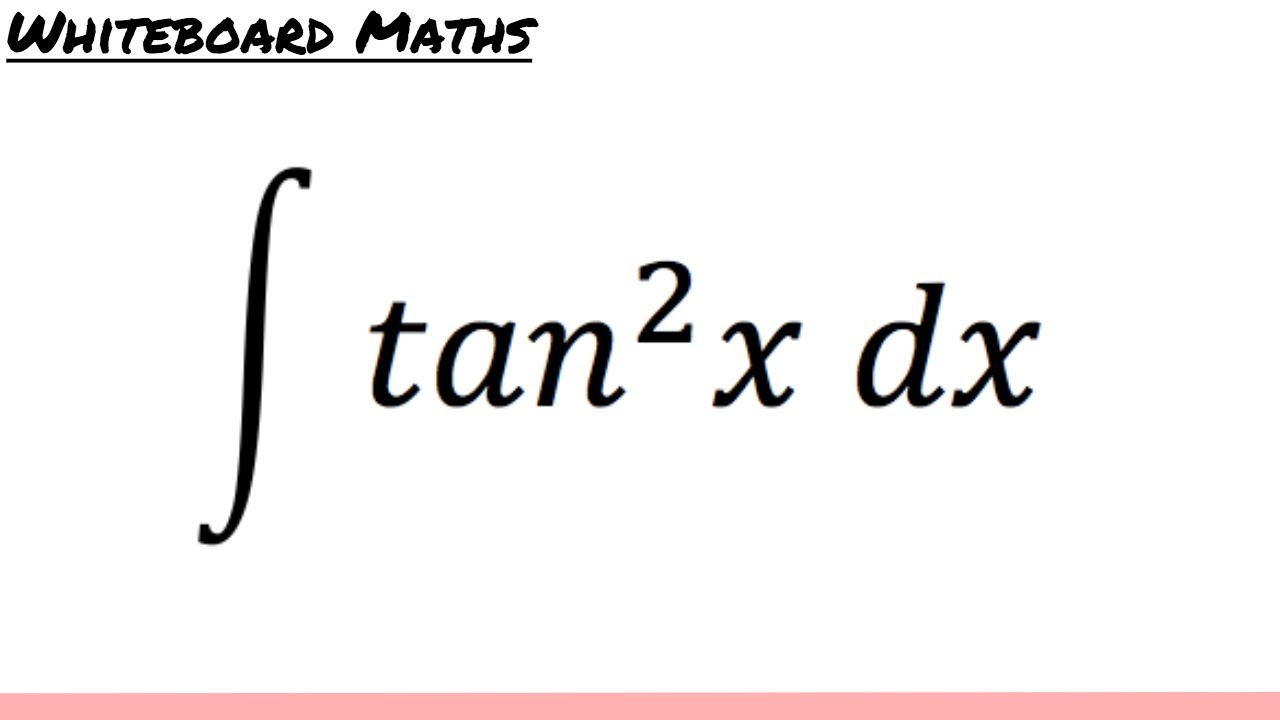



Integral Of Tan 2 X Youtube




Integral Of Tan X Video Khan Academy




Integral Of Sec 2 X Sqrt 1 Tan 2 X Using The Arcsine Function Math Videos Maths Exam Calculus




Integrate The Function X 3sin Tan 1x 4 1 X 8




Find The Antiderivatives Of The Following 1 Gauthmath



Http Pue Kar Nic In Pue Pdf Files Recogn Ipu Iiqb 35 Ch7 Pdf
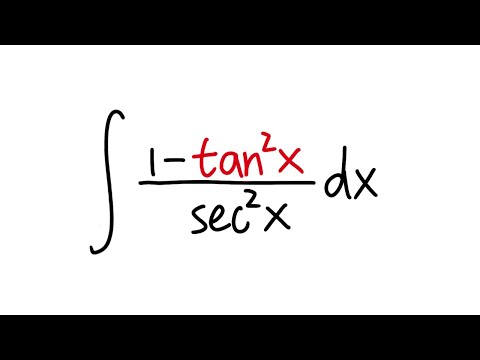



Q45 Integral Of 1 Tan 2x Sec 2x Youtube




Substitution Rule



Http Macs Citadel Edu Chenm 132 Dir 11sum Dir Lect4 1 6 Pdf




Mastering Olympiad Mathematics Putnam Definite Integral Hard Problem Evaluate Displaystyle Int 0 Frac Pi 2 Frac Dx 1 Tan X Sqrt 2




How Do You Find The Antiderivative Of Int Sin 2xdx Socratic



What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora
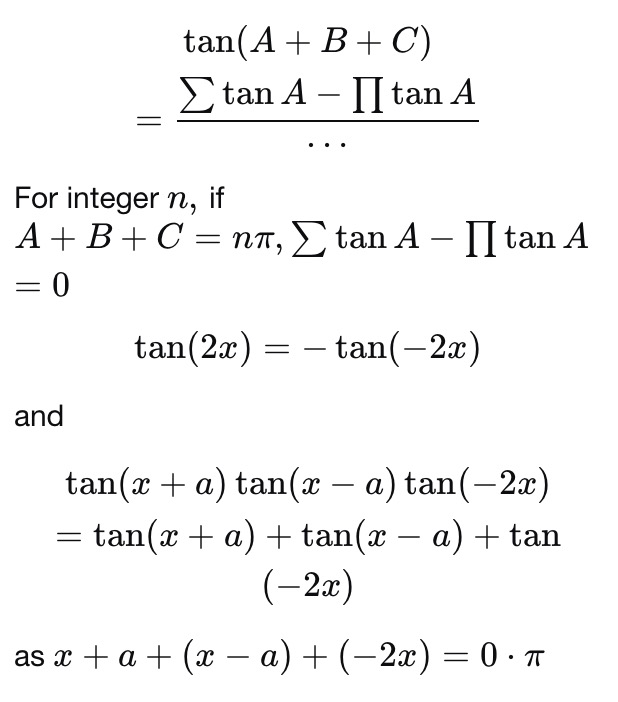



Please Integrate This And Send Me The Solution Maths Doubts Goiit Com
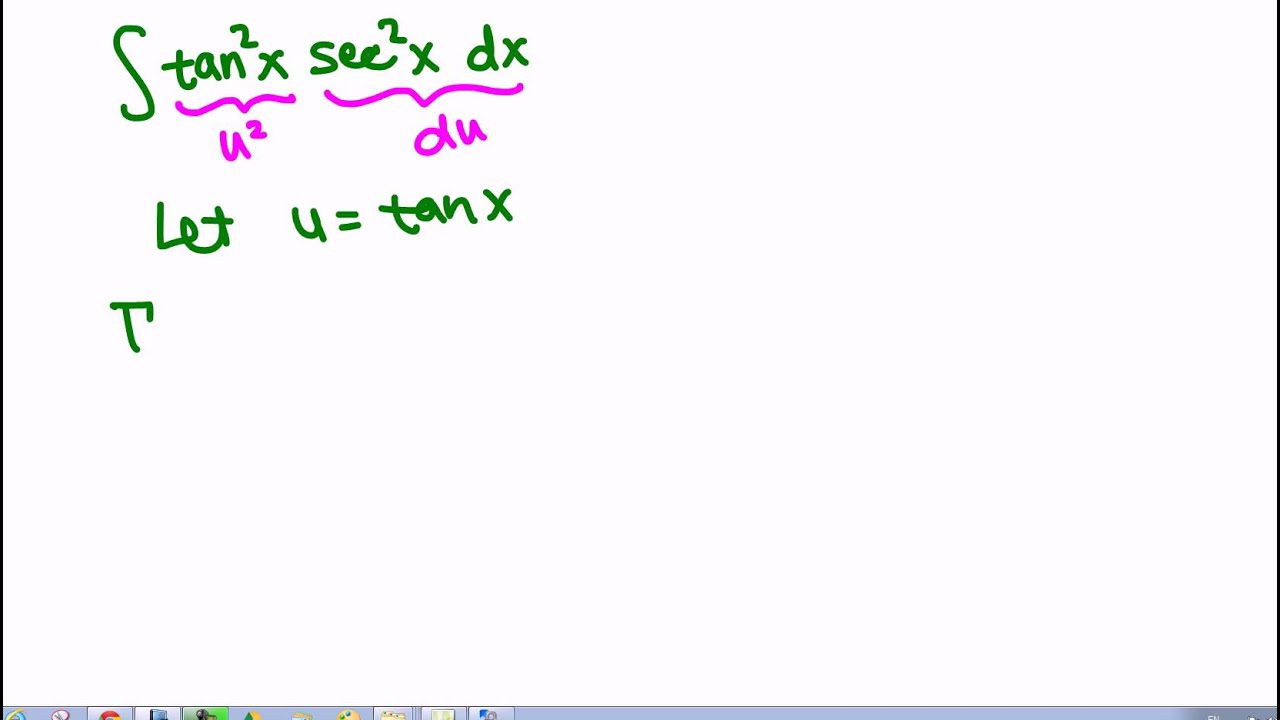



Integration Of Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube




Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube




Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia




Indefinite Integral
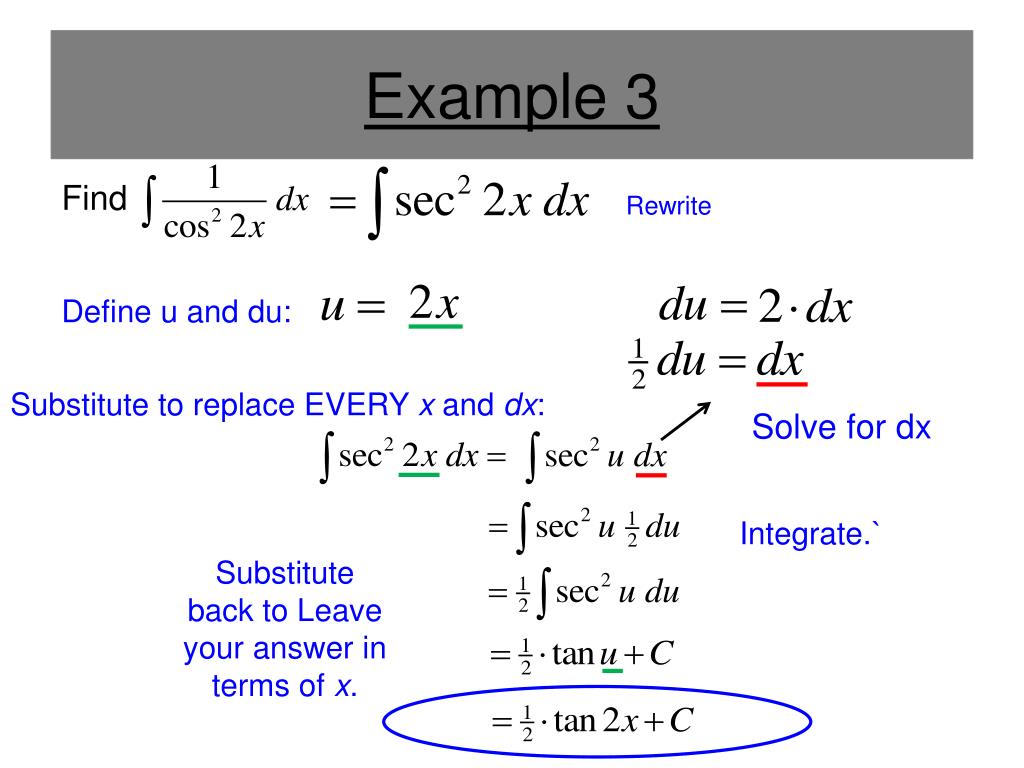



Ppt Section 4 5 Integration By Substitution Powerpoint Presentation Id




تخته سفید Sect 5 5 23 Integral Of Sec 2x Tan 3x




8 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration As
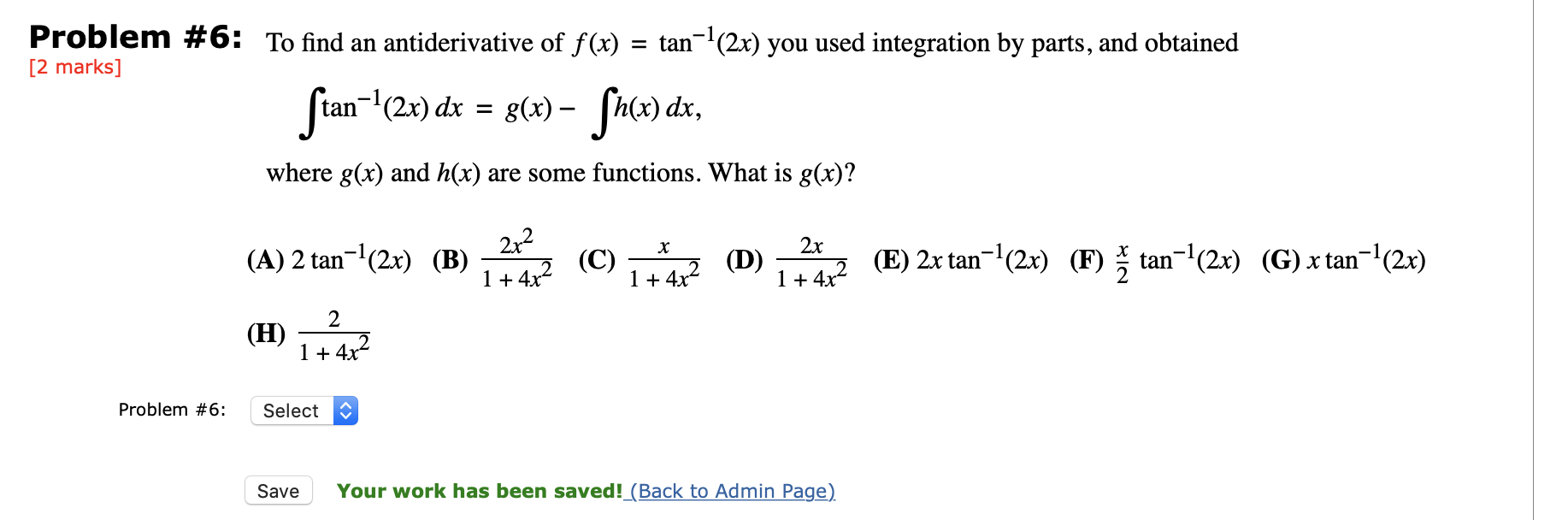



Problem 6 To Find An Antiderivative Of F X Chegg Com




7 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration 7




How To Integrate 2x Sec 3 X 2 3 Tan X 2 3 Quora
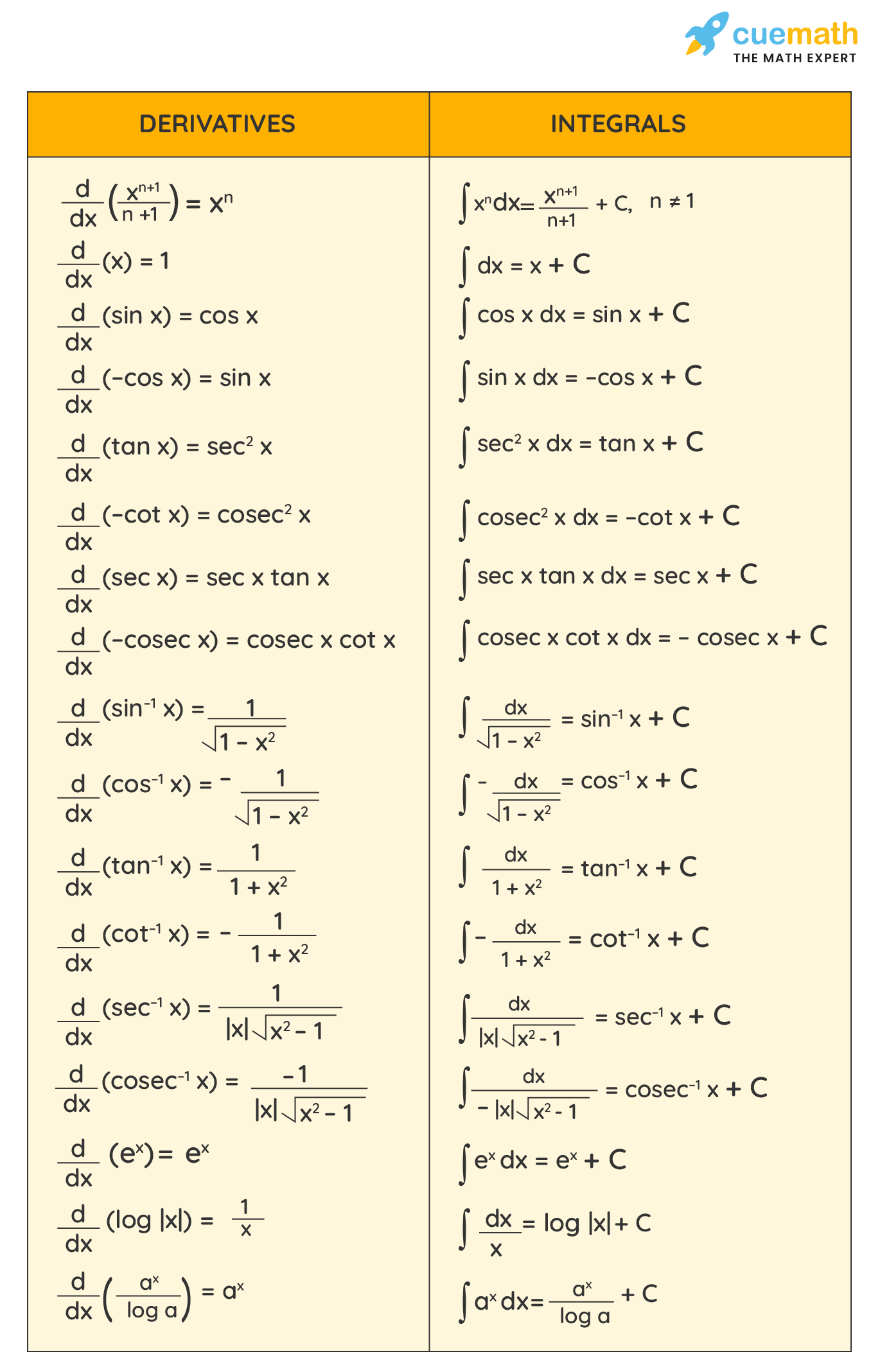



Antiderivative Calculator Examples Online Antiderivative Calculator




Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube




Integration Calculus 2



Integral Of Sec 6 X Tan 2 X Dx




Integrate Tanx Tan 2x Tan3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com




Q77 Integral Of X Tan 2x Youtube




The Integral Of Sec 4 X Tan X Mathematics Stack Exchange




The Integral Int Sec 2x Secx Tanx 9 2 Dx Equals For Some Arbitrary Constant K Dot 1 Secx Tanx 11 2 1 11 1 7 Secx Tanx 2 K 1 Secx Tanx 1 11 1 11 1 7 Secx Tanx 2 K 1 Secx Tanx 11 2 1 11 1 7 Secx Tanx 2 K 1




How Do You Evaluate The Integral 1 Tan X 3 Sec 2 X Dx Within The Range 0 Pi 4 Socratic




Evaluate Int Secx Secx Tanx Dx




Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像




Evaluate Integral Tan 6 2x Sec 4 2x Dx If We Chegg Com




Ex 7 3 15 Integrate Tan3 2x Sec 2x Class 12 Ncert Ex 7 3




Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia
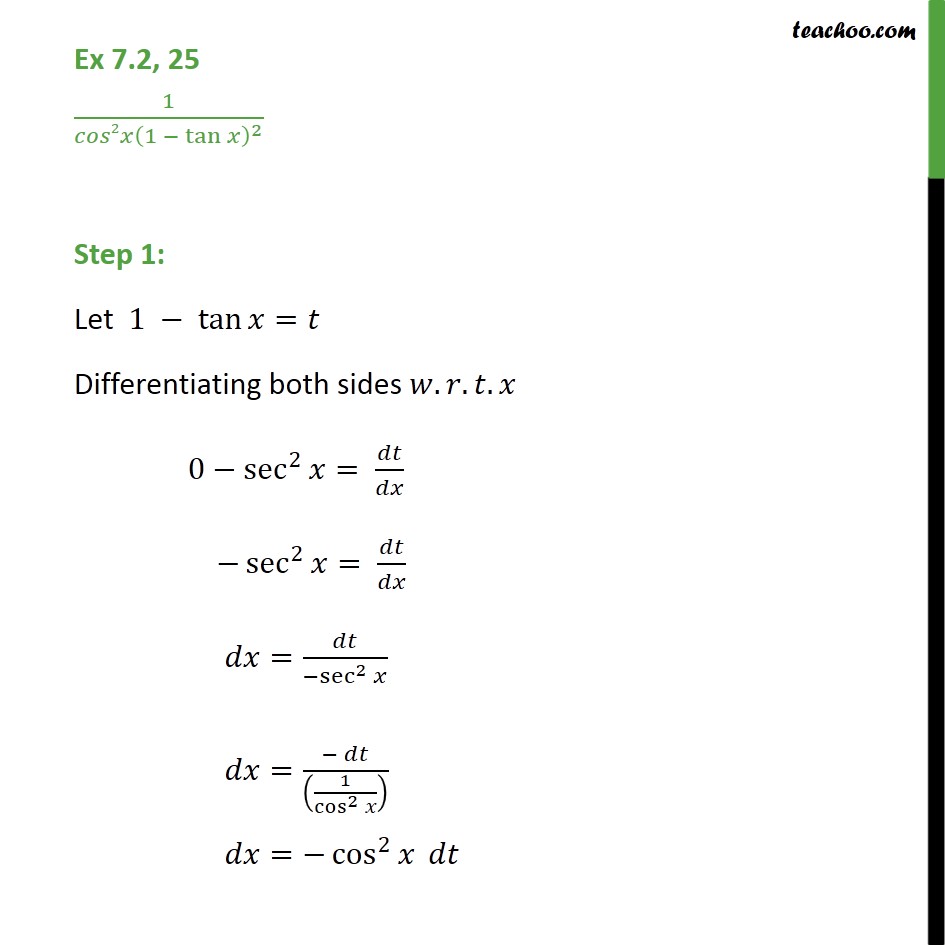



Ex 7 2 25 Integrate 1 Cos 2 X 1 Tan X 2 Ex 7 2




Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia



Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube




Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x 3 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 2



Dtube How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Steemit




Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia
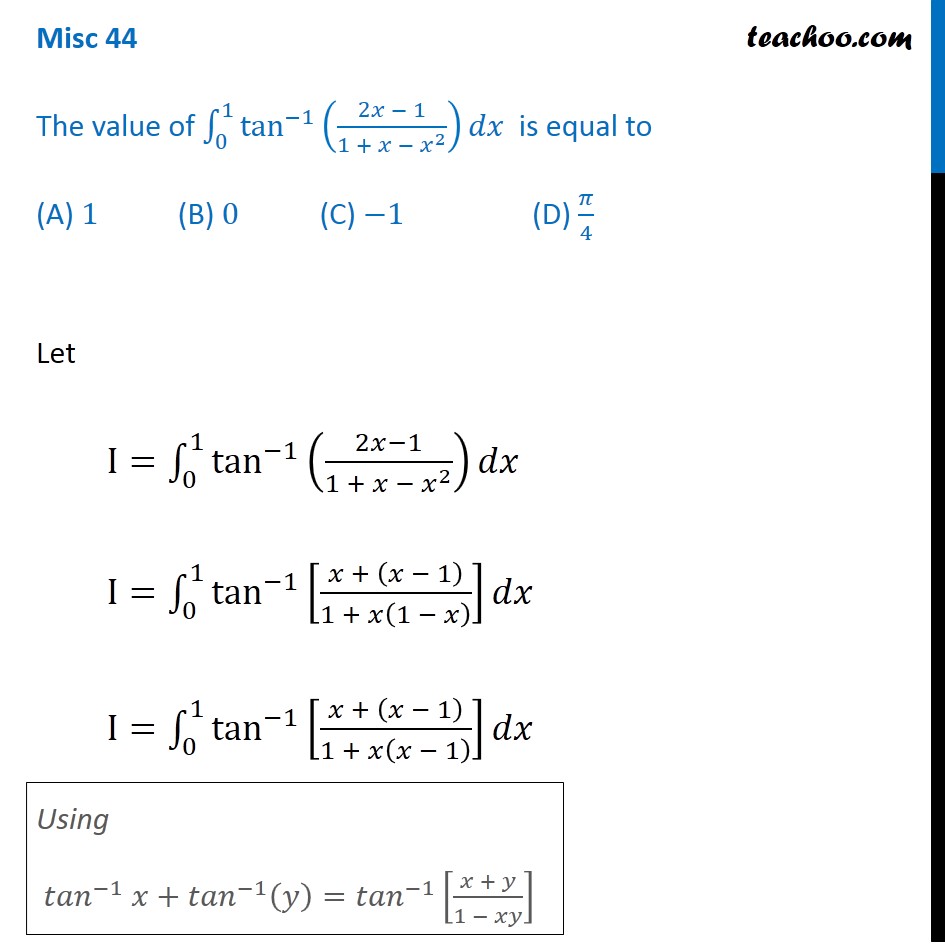



Misc 44 Mcq Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 8 2 chapter i V Pdf Sequence 2




Answered 1 Vxx 11 Vx 1 4 Verify By Bartleby




Test4 Solution



What Is The Integral Of Sec 2x Tan 2x Dx Brainly Com



What Is The Antiderivative Of Tan Mccnsulting Web Fc2 Com




Solving The Integral Of Cos 2x Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Finding The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Section 5 3 The Definite Integral Ppt Video Online Download



1
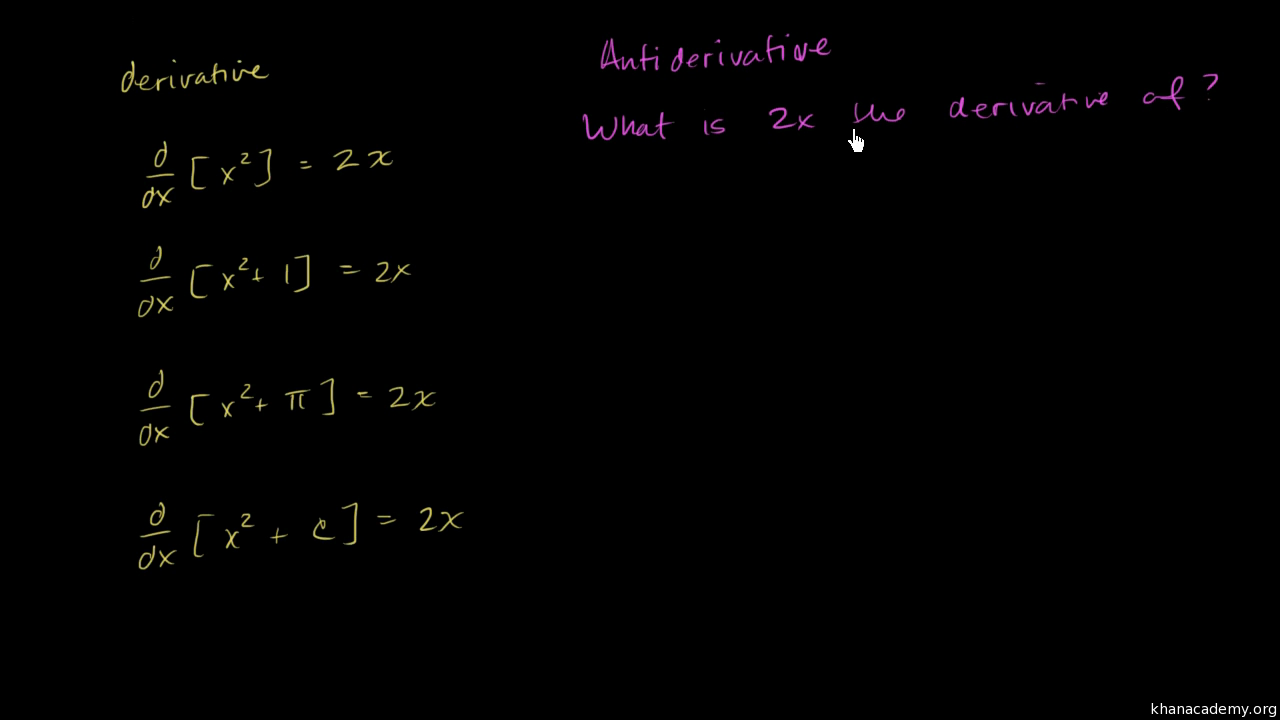



Antiderivatives And Indefinite Integrals Video Khan Academy




Ex 7 6 24 Mcq Integrate E X Sec X 1 Tan X Dx Is A E X Cos X



How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube



How To Integrate Tan 2x Youtube



1




Integral Xsinx 1 Cos 2 X Dx I Get That In Walfram Www Wolframalpha Com Input I Integral Xsinx 2f 281 2bcos 2x 29 But It Does Not Help Enotes Com
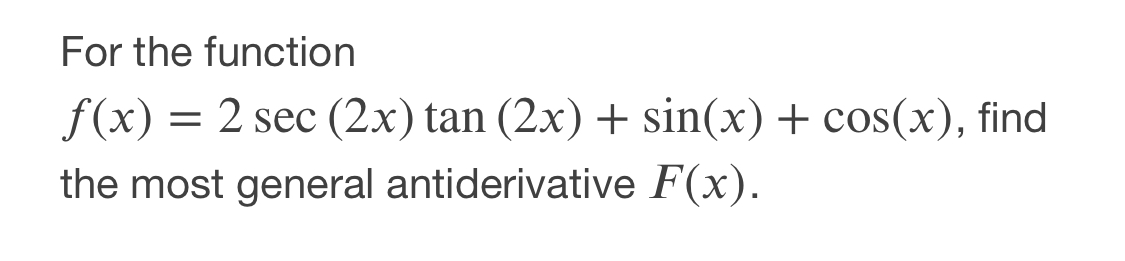



Answered For The Function F X 2 Sec 2x Tan Bartleby




Find The Derivative Of F X Integral 2tan X 0 2t 4 Chegg Com
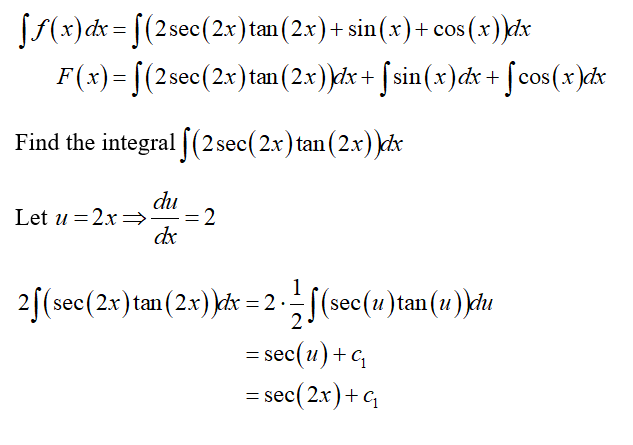



Answered For The Function F X 2 Sec 2x Tan Bartleby
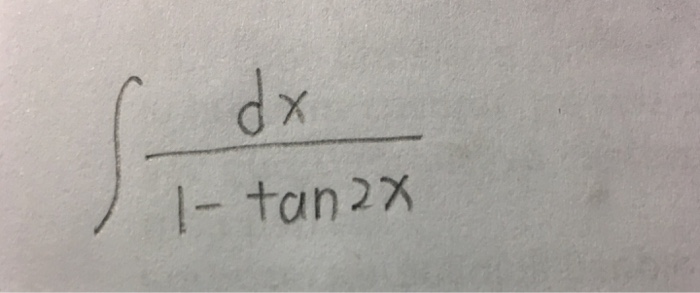



Integral Dx 1 Tan 2x Chegg Com




Integration With U Substitution The Integral Of Sqrt Tan 4x Sec 2 4x Math Videos Calculus Integrity
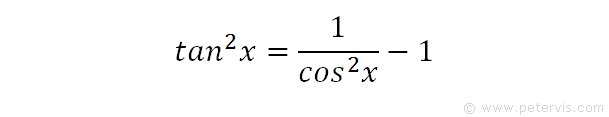



Integrate Tan 2x



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿